In this article, Spiritual Culture explores the intricacies of Julian dates, sheds light on conversion methods, and discusses applications in different domains. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or professional, this guide will equip you with the necessary knowledge and tools to navigate Julian dates effectively.
Understanding Julian Dates
Definition of Julian Dates
Julian dates represent a continuous count of days since a specific starting point, known as the Julian Day Number (JDN), which is traditionally set at January 1, 4713 BCE in the Julian calendar. In scientific contexts, Julian dates simplify date calculation by converting calendar dates into a single numeric sequence. For instance, the Julian date for January 1, 2024, is 2460168, indicating it has been 2,460,168 days since the defined starting point.
Historical Context of Julian Dates
Originating from the Julian calendar, devised by Julius Caesar in 46 BCE, Julian dates were designed to address the inaccuracies of the Roman calendar. The system later evolved into what we now refer to as the Gregorian calendar, established by Pope Gregory XIII in 1582. Despite the transition to the Gregorian calendar, Julian dates remain widely used in astronomy, scientific research, and other technical fields due to their precision and ease of calculation.
Purpose and Use in Various Fields
Julian dates serve multiple purposes across various disciplines:
- Astronomy: They allow for precise calculations of celestial events.
- History: They provide a consistent framework for event dating across different calendar systems.
- Scientific Research: Many disciplines, including geology and paleontology, utilize Julian dates for data comparisons.
- Computing: Julian dates facilitate date arithmetic in programming and data analysis.
Julian Date Conversion Methods
Manual Calculation of Julian Dates
To manually calculate a Julian date from a Gregorian date, you can use the following steps:
- Identify the Date: Choose a Gregorian date (e.g., July 20, 2024).
- Calculate the Julian Day Number: Use the formula based on the Gregorian date components (year, month, day).
- Use The Julian Day Calculation Formula:
- For the Gregorian calendar:
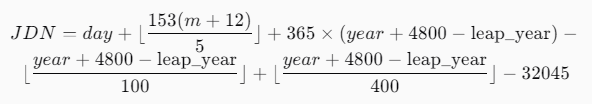 Where:
Where: - m = month (if month is January or February, count it as 13 or 14 of the previous year)
- leap_year = 1 if the year is divisible by 4, except for end-of-century years that are not divisible by 400.
- For the Gregorian calendar:
- Obtain Julian Date: The result is the Julian date.
Using Online Julian Date Converters
Various online tools can facilitate easy conversions between Julian and Gregorian dates. Many websites allow users to input a Gregorian date and output the corresponding Julian date instantly. These tools often provide additional functionality, including conversions to Modified Julian Dates (MJD) and the ability to handle various date formats.
Input Formats for Julian Date Conversion
When using online converters, be aware of the acceptable input formats. Most tools accept:
- Standard Gregorian date formats (MM/DD/YYYY, DD/MM/YYYY)
- Julian date formats (JD or JDN)
- Options for leap years or adjustments if relevant
Converting Gregorian Dates to Julian Dates
Steps to Convert Gregorian Dates
To convert a Gregorian date to its Julian equivalent:
- Identify Components: Break down the Gregorian date into day, month, and year.
- Adjust for the Year: If the month is January or February, consider it as part of the previous year.
- Compute the JDN: Use the aforementioned formula to calculate the Julian Day Number.
- Read the Output: The computed JDN represents the Julian date.
Example Calculation for Gregorian to Julian
Let’s say we want to convert June 15, 2024, to its Julian date:
- Components: Day = 15, Month = 6, Year = 2024.
- Calculate:
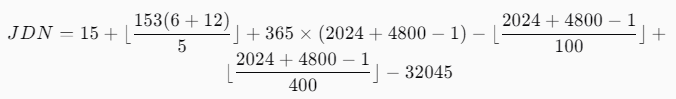 Simplifying this calculation yields the Julian date of 2460420 for June 15, 2024.
Simplifying this calculation yields the Julian date of 2460420 for June 15, 2024.
Modifications of Julian Dates
Overview of Modified Julian Date (MJD)
The Modified Julian Date (MJD) is a system that simplifies the Julian date by offsetting it. The MJD is defined as the Julian Date minus 2400000.5. This adjustment makes it more manageable to work with, especially in scientific calculations. For example, MJD 60000 corresponds to JD 2400000.5 + 60000, which can be used easily in data tables and computational models.
Using MJD in Scientific Applications
MJD is predominantly used in astronomy, where precise timing is vital for observations and calculations. Many astronomical software packages and databases utilize MJD for data storage and processing, allowing researchers to manage time in a consistent and standardized manner.
Applications of Julian Dates in Astronomy
Importance of Julian Dates in Astronomical Calculations
Julian dates are critical in astronomy due to their uniformity. Astronomers use JD or MJD to timestamp observations efficiently, enabling precise measurements of celestial events, such as eclipses or planetary alignments. The linearity of Julian dates eliminates the complexities of calendar conversions, streamlining data analysis.
Case Studies: Julian Dates in Astronomical Software
Several popular astronomical software systems—like Astropy and SkySafari—use Julian dates. For example, Astropy allows users to convert and manipulate dates effortlessly, utilizing Julian dates as a foundational element. Such systems provide functionality for calculating the positions of celestial bodies, tracking their movements, and predicting phenomena like meteor showers.
Tools and Resources for Julian Date Conversion
Recommended Online Tools and Software
There are multiple online tools available for Julian date conversion, such as:
- Time and Date Julian Date Converter: Offers a user-friendly interface for date conversions, including MJD.
- COSMOS Julian Date Calculator: A specialized tool for astronomers that calculates JD and MJD.
- NASA Julian Date Converter: Useful for those working with NASA data or looking for precise astronomical computations.
Mobile Apps for Julian Date Conversion
For convenience on mobile devices, several apps are available:
- Julian Date Converter (iOS/Android): A simple tool for on-the-go conversions.
- Astronomy Tools (iOS/Android): Apps that integrate several astronomical functions, including Julian date conversions.
Conclusion
Understanding how to read and convert Julian dates is essential for various applications, particularly in scientific and astronomical contexts. By using the methods outlined in this article, including both manual calculations and online tools, you can confidently navigate different date systems. Whether you are a hobbyist astronomer, a student, or a professional researcher, having a firm grasp of Julian dates will be invaluable in your work.
By leveraging the tools and knowledge shared here, you can ensure accurate date calculations and enhance your understanding of the temporal dimensions in scientific studies. The Julian calendar and its derivatives continue to play a pivotal role in how we measure and understand time, making them relevant in today’s technologically advanced world.


