The Hindu calendar is an ancient system of timekeeping that has been in use for thousands of years. It is based on both the lunar and solar cycles, with the lunar months following the phases of the moon, and the solar year synchronizing with the solar cycle. The Hindu calendar has 12 months, with names such as Chaitra, Vaisakha, Jyaistha, etc., and each month consists of either 29 or 30 days.
The Hindu calendar has several regional variations and different calendars are used in different regions of India, such as the Bengali, Tamil, and Telugu calendars. The calendar is used to determine the dates of religious festivals, such as Diwali, Holi, and Navaratri, as well as the dates of other important events, such as weddings and business transactions.
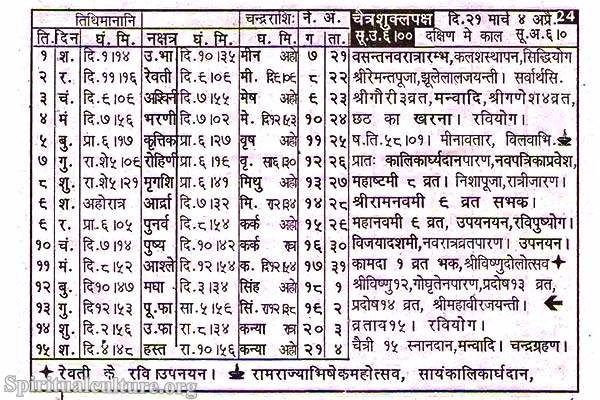
In addition to its religious and cultural significance, the Hindu calendar also plays an important role in agriculture, as it is used to determine the timing of planting and harvesting crops. The Hindu calendar is a complex system that reflects the deep understanding of astronomy and timekeeping that was developed in ancient India.
The Hindu calendar also has several different eras, or yugas, that are used to mark the passage of time. The current era is called the Kali Yuga, which is believed to have begun in 3102 BCE. The Hindu calendar also includes a 60-year cycle of names for each year, which is used to determine the auspicious timing of events.
In modern times, the Hindu calendar is used primarily in Hindu religious observances and to determine the dates of festivals and other important events. It continues to play an important role in Hindu culture and provides a shared sense of identity and tradition for Hindus around the world.
Overall, the Hindu calendar is a rich and complex system that reflects the ancient knowledge and traditions of Hindu culture. It serves as a powerful symbol of the continuity and richness of Hindu heritage and continues to play an important role in the lives of Hindus today.




